
It was the most recent, stable release when this was written. This type of scenario is why many enterprises use Red Hat. To understand why this is important, consider what happens when your application is in production and a critical security vulnerability in a core library (for example SSL/TLS) is discovered. However, support is important to those who have to deploy and operate the applications you write. During development, support might not seem that important to you.

This article uses Red Hat Software Collections because these give you a current Python installation that is built and supported by Red Hat. There are a number of different ways to get Python 3 installed on RHEL. Other tips and FAQs for working with Python and software collections on RHEL 7 are also covered.
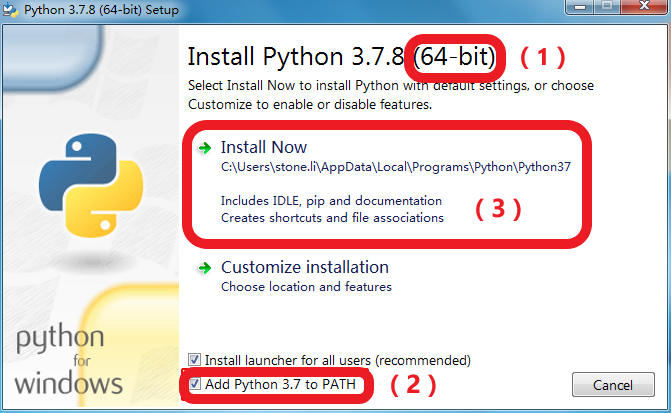
Using Python virtual environments is a best practice to isolate project-specific dependencies and create reproducible environments. Note: For RHEL 8 installs, See Python on RHEL 8. After following the steps in this article, you should be in a good position to follow many Python guides and tutorials using RHEL. This article shows how to install Python 3, pip, venv, virtualenv, and pipenv on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
